GC columns Selection
Stationnary Phase
Choosing a stationary phase is the most important step in selecting a column.
Select the least polar phase that will perform the separation you require.
Synonymous use of the terms polarity and selectivity is not accurate, but it is very common.
Selectivity is determined by the physicochemical interactions of the solute molecules with the stationary phase. Polarity is determined by the structure of the stationary phase. Polarity does have an effect on separation; however, it is only one of the many stationary phase properties that influence peak separation.
Selectivity can be thought of as the ability of the stationary phase to differentiate between two solute molecules by differences in their chemical or physical properties. Separation is obtained if the interactions between the stationary phase and solutes are different.
For liquid or gum stationary phase (polysiloxanes and polyethylene glycols), there are three major interactions: dispersion, dipole, and hydrogen bonding. The following is a simplified and condensed explanation of the interactions for polysiloxane and polyethylene glycol stationary phases.
| GC Columns Stationary Phase Applications Guide | |||||
| Application | Composition | Polarity | Approximate Temp Range (°C) | Similar Phases | |
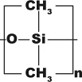
| Amines, hydrocarbons, pesticides, PCBs, phenols, sulfur compounds, flavors and fragrances | 100% Dimethylpolysiloxane | Non-polar | From -60 to 325/350 |
UptiBond-1P, HP-1ms, DB-1ms, HP-1, DB-1, BP-1, SPB-1, CP-Sil 5, Rtx-1, OV-1, SE-30, 007-1, ZB-1 | |
 |
|||||
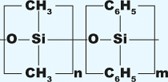
| Semivolatiles, alkaloids, drugs, FAMEs, halogenated compounds, pesticides, herbicides | 5% Phenyl 95% dimethylpolysiloxane | Non-polar | From -60 to 325/350 |
UptiBond 5P, HP-5ms, DB-5, HP-5, SPB-5, XTI-5, Mtx-5, CP-Sil 8CB, SE-54, Rtx-5, BPX-5, MDN-5, Rtx-5ms, BP-5, ZB-5 | |
 |
|||||
| Semivolatiles, alkaloids, drugs, FAMEs, halogenated compounds, pesticides, herbicides | 5% Phenyl 95% dimethylpolysiloxane | Non-polar | From -60 to 325/350 |
DB-5ms, Rtx-5ms, Rtx-5Sil MS, Rxi-5ms, Rxi-5Sil MS, VF-5ms, PTE-5, CP-Sil 8 CB Low Bleed/MS, BPX-5, AT-5ms, ZB-5ms, SLB-5ms, Equity-5 | |
 |
|||||
| Aroclors, alcohols, pesticides, VOCs | 6% Cyanopropyl-phenyl 94% dimethylpolysiloxane | Mid-polar | From -20 to 280/300 |
UptiBond 1301, DB-1301, Rtx-1301, PE-1301, VF-1301ms | |
 |
|||||
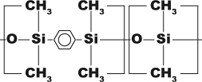
| CLP-pesticides, aroclors, pharmaceuticals, drugs of abuse | 35% Phenyl 65% dimethylpolysiloxane | Mid-polar | From 40 to 300/320 |
DB-35, HP-35, Rtx-35, SPB-35, AT-35, Sup-Herb, MDN-35, BPX-35 | |
 |
|||||
| CLP-pesticides, aroclors, pharmaceuticals, drugs of abuse | 35% Phenyl 65% dimethyl arylene siloxane | Mid-polar | From 50 to 340/360 |
DB-35ms, Rtx-35, Rtx-35ms, VF-35ms, SPB-35, AT-35, Sup-Herb, MDN-35, BPX-35 | |
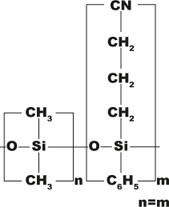
| Pesticides, herbicides, TMS sugars, aroclors | 14% Cyanopropyl-phenyl 86% dimethylpolysiloxane | Mid-polar | From -20 to 280/300 |
UptiBond 1701, DB-1701, DB-1701P, SPB-1701, CP-Sil 19 CB, Rtx-1701, CB-1701, OV-1701, 007-1701, BPX-10 | |
 |
|||||
| Drugs, glycols, pesticides, steroids | 50% Phenyl 50% dimethylpolysiloxane | Mid-polar | From 40 to 280/300 |
UptiBond 17, HP-50+, DB-17, Rtx-50, CP-Sil 19 CB, BPX-50, SP-2250 | |
| Drugs, glycols, pesticides, steroids | 50% Phenyl 50% dimethyl arylene siloxane | Mid-polar | From 40 to 320/340 |
DB-17ms, HP-50+, Rtx-50, VF-17ms, 007-17, SP-2250, SPB-50, BPX-50, SPB-17, AT-50 | |
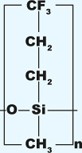
| Residual solvents, pesticides, herbicides | 35% Trifluoropropyl 65% dimethylpolysiloxane | Polar | From 30 to 300/320 |
DB-200 , Rtx-200, VF-200ms | |
 |
|||||
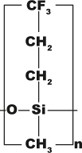
| EPA Methods 8140 and 609 | 50% Trifluoropropyl 50% dimethylpolysiloxane | Polar | From 45 to 240/260 |
UptiBond 210, DB-210, SP-2401 | |
 |
|||||
| FAMEs, alditol acetates, neutral sterols | 50% Cyanopropyl-phenyl 50% dimethylpolysiloxane | Polar | From 40 to 220/240 |
UptiBond 225, DB-225ms, DB-225, SP-2330, CP-Sil 43 CB, OV-225, Rtx-225, BP-225, 007-225 | |
 |
|||||
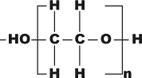
| Alcohols, free organic acids, solvents, essential oils, flavors and fragrances | Polyethylene glycol | Polar | From 40 to 260/270 |
HP-INNOWax, HP-20M, SUPELCOWAX 10, CP-WAX 52 CB, SUPEROX II, CB-WAX, Stabilwax, BP-20, 007-CW, Carbowax, DB-WAXetr, ZB-WAX | |
 |
|||||
| Solvents, glycols, alcohols | Polyethylene glycol | Polar | From 20 to 250/260 |
UptiBond WAX, DB-WAX, HP-20M, SUPELCOWAX 10, CP-WAX 52 CB, SUPEROX II, CB-WAX, Stabilwax, BP-20, 007-CW, Carbowax, HP-INNOWax, Rtx-WAX, ZB-WAX, VF-WAXms | |
| Amines, basic compounds | Polyethylene glycol-base modified | Polar | From 60 to 220/240 |
UptiBond Amine, CAM, Stabilwax-DB, Carbowax Amine | |
| Organic acids, alcohols, aldehydes, ketones, acrylates | Polyethylene glycol-acid modified | Polar | From 40 to 250 |
UptiBond FFAP, HP-FFAP, DB-FFAP, OV-351, SP-1000, Stabilwax-DA, 007-FFAP, Nukol | |
| FAMEs (requiring cis/trans resolution) | 50% Cyanopropyl 50% dimethylpolysiloxane | Polar | From 40 to 250/260 |
DB-23, SP-2330, Rtx-2330, 007-23, AT-Silar, BPX-70, SP-2340, VF-23ms | |
 |
|||||
| Chiral compounds (general purpose) | 30%-heptakis (2,3-di-O-methyl-6-O-t-butyl dimethylsilyl)-B-cyclodextrin in DB-1701 | Mid-polar | From 35 to 260/280 |
CycloSil-ß, LIPODEX C, Rt-ß DEXm, ß-DEX 110, ß-DEX 120 | |
| Chiral compounds (using a Nitrogen selective detector, NPD) | beta-Cyclodextrin in phenylbased stationary phase | Mid-polar | From 30 to 240/250 |
HP-Chiral ß, LIPODEX C, Rt-ß DEXm, ß-DEX 110, ß-DEX 120 | |
| Permanent and noble gases. Argon and oxygen separation at 35°C | 5Å molecular sieve zeolite | From -60 to 300 |
HP-PLOT Molesieve | ||
| C1-C6 hydrocarbons in natural gas, refinery gas, fuel gas, synthetic gas, dienes | Aluminum Oxide KCl deactivated | Least polar | From -60 to 200 |
HP-PLOT Al2O3 KCl, CP-Al2O3/KCl PLOT, Rt-Alumina PLOT, Alumina PLOT, Al2O3/KCl | |
| C1-C6 hydrocarbons in natural gas, refinery gas, fuel gas, synthetic gas, dienes | Aluminum Oxide "Sodium Sulfate" deactivated | Mid-polar | From -60 to 200 |
HP-PLOT Al2O3 S, CP-Al2O3 PLOT Na2SO4 | |
| C1-C6 hydrocarbons in natural gas, refinery gas, fuel gas, synthetic gas, dienes | Aluminum Oxide with proprietary deactivation | Most polar | From -60 to 200 |
GS-Alumina, Al2O3/KCl, Al2O3/Na2SO4, Rt-Alumina PLOT, Alumina PLOT | |
| Hydrocarbons including isomers, CO2, methane, air/CO, water, polar solvents, sulfur compounds | Polystyrene-divinylbenzene | From -60 to 270/290 |
HP-PLOT Q, CP PoraPLOT Q, CP PoraPLOT Q-HT, Rt-QPLOT, SupelQ PLOT, GS-Q | ||
| C1-C7 hydrocarbons, CO2, methane, air/CO, water, oxygenates, amines, solvents, alcohols, ketones, aldehydes | Divinylbenzene/ethylene glycol dimethacrylate | From -60 to 19 |
HP-PLOT U, PoraPlot U, RTU PLOT | ||
| C1-C12 hydrocarbons, CO2, trace-level sulfurs, hydride gases, inorganic gases, halocarbons, SF6, oxygen/nitrogen separation at -80°C | Proprietary, bonded silica-based | From -80 to 260/300 |
GS-GasPro, CP-Silica PLOT | ||
| Oxygenates | Proprietary phase, high selectivity | To 350 | GS-OxyPLOT, CP-LowOX | ||
| C1-C5 hydrocarbons, CO2, air/CO, trace acetylene in ethylene, methane | Bonded monolithic carbon layer | From 0 to 360 |
GS-CarbonPLOT, Carbopack, CLOT, Carboxen-1006 PLOT, CP-CarboPLOT P7 | ||
| European Commission regulated polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons | Proprietary phase | Mid-polar | From 40 to 320/340 |
DB-EUPAH | |
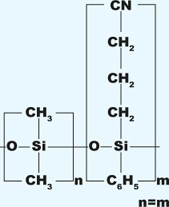
| Volatile Priority Pollutants, EPA Method 502.2 | 6% Cyanopropyl-phenyl, 94% dimethylpolysiloxane | Mid-polar | From -20 to 260 |
UptiBond 624, DB-624, AT-624, Rtx-624, PE-624, 007-624, 007-502, CP-624, ZB-624, VF-624ms | |
| Volatile Organic Compounds using MSD, ELCD/PID | Proprietary phase | Non-polar | From -10 to 260 |
DB-VRX, VOCOL, NON-PAKD, Rtx-Volatiles, PE-Volatiles, 007-624, HP-624, CP-624, Rtx-VRX, Rtx-VGC | |
| CLP Pesticides, Chlorinated Herbicides, PCBs, 508.1 Pesticides | 35% Phenyl, 65% dimethyl arylene siloxane | Mid-polar | From 50 to 340/360 |
DB-35ms, Rtx-35, Rtx-35ms, VF-35ms, SPB-35, AT-35, Sup-Herb, MDN-35, BPX-35 | |
Stationary Phase Interactions
| Functional Group | Dispersion | Dipole | Hydrogen Bonding |
| Methyl | Strong | None | None |
| Pheny | Strong | None to Weak | Weak |
| Cyanopropyl | Strong | Very Strong | Moderate |
| Trifluoropropyl | Strong | Moderate | Weak |
| PEG | Strong | Strong | Moderate |
| Column length in meters (m) | |
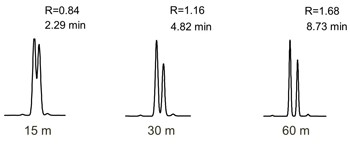 |
Always try to select the shortest column length that will provide the required resolution for the application. If the maximum column length available is being used, and resolution of the sample mixture is still inadequate then try changing the stationary phase or internal diameter The resolution is proportional to the square root of the column efficiency. Therefore, doubling the column length will only increase the resolving power of the column by approximately 40%. |
| Inner diameter (ID) or internal diameter in millimeters (mm) | |
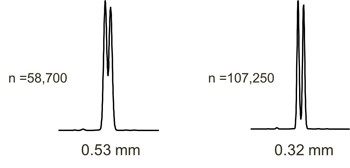 |
The smaller the diameter the greater the efficiency, hence better resolution Fast column (0.1mm) are used for faster analysis because the same resolution can be achieved un a shorter time. |
| Film thickness in micrometers (µm) | |
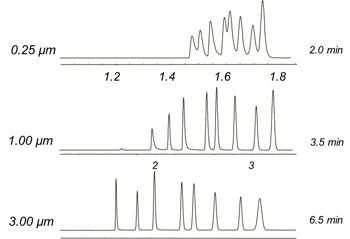 |
For samples with a variation in solute concentration, a thicker film column is recommended. This will reduce the possibility of broad overloaded peaks co-eluting with other compounds of interest. If the separation of two solutes is sufficient and co-elution is still unlikely, even with large differences in concentration; then a thinner film can be used. The greater the film thickness the greater the retention of solutes, therefore the higher the elution temperature As a rule, doubling the film thickness results in an increase in elution temperature of approximately 15-20° under isothermal conditions. Using a temperature program, the increase in elution temperature is slightly less. |